A few months ago I decided to add syntax highlighting capabilities to a piece of software that I have been working on. Since it is a PyQt based application, the obvious choice for implementing syntax highlighting was to use Qt’s QSyntaxHighlighter. Unfortunately, there weren’t many examples around that implemented syntax highlighting in Python, so I decided to post my own.
The Python file used in this example is available here.
To implement syntax highlighting, we need to subclass
QSyntaxHighlighter, reimplement the highlightBlock function, and
specify several highlighting rules. Generally, a rule consists of a
QRegExp pattern and a QTextCharFormat instance. For this example, the
syntax rules are based on the R statistical programming language. The
various rules can be stored using a Python list.
import sys
from PyQt4.QtGui import *
from PyQt4.QtCore import *
class MyHighlighter( QSyntaxHighlighter ):
def __init__( self, parent, theme ):
QSyntaxHighlighter.__init__( self, parent )
self.parent = parent
self.highlightingRules = []
keyword = QTextCharFormat()
keyword.setForeground( Qt.darkBlue )
keyword.setFontWeight( QFont.Bold )
keywords = QStringList( [ "break", "else", "for", "if", "in",
"next", "repeat", "return", "switch",
"try", "while" ] )
for word in keywords:
pattern = QRegExp("\\b" + word + "\\b")
rule = HighlightingRule( pattern, keyword )
self.highlightingRules.append( rule )
MyHighlighter is the subclassed QSyntaxHighlighter class, and will
contain our reimplemented highlightBlock function. The above example
is for the keyword rule, which recognizes the most common R keywords.
We give keyword a bold, dark blue font. For each keyword, we assign
the keyword and the specified format to a HighlightingRule object (see
the attached Python file) and append the object to our list of rules.
We can specify further syntax rules, including reservedClasses,
assignmentOperators, and numbers:
reservedClasses = QTextCharFormat()
reservedClasses.setForeground( Qt.darkRed )
reservedClasses.setFontWeight( QFont.Bold )
keywords = QStringList( [ "array", "character", "complex",
"data.frame", "double", "factor",
"function", "integer", "list",
"logical", "matrix", "numeric",
"vector" ] )
for word in keywords:
pattern = QRegExp("\\b" + word + "\\b")
rule = HighlightingRule( pattern, reservedClasses )
self.highlightingRules.append( rule )
assignmentOperator = QTextCharFormat()
pattern = QRegExp( "(<){1,2}-" )
assignmentOperator.setForeground( Qt.green )
assignmentOperator.setFontWeight( QFont.Bold )
rule = HighlightingRule( pattern, assignmentOperator )
self.highlightingRules.append( rule )
number = QTextCharFormat()
pattern = QRegExp( "[-+]?[0-9]*\.?[0-9]+([eE][-+]?[0-9]+)?" )
pattern.setMinimal( True )
number.setForeground( Qt.blue )
rule = HighlightingRule( pattern, number )
self.highlightingRules.append( rule )
After a QSyntaxHighlighter object is created, its highlightBlock()
function will be called automatically whenever it is necessary by the
rich text engine, highlighting the given text block. To perform the
actual formatting, the QSyntaxHighlighter class provides the setFormat
function. This function operates on the text block that is passed as
argument to the highlightBlock function. The specified format is
applied to the text from the given start position for the given length.
The formatting properties set in the given format are merged at display
time with the formatting information stored directly in the document.
def highlightBlock( self, text ):
for rule in self.highlightingRules:
expression = QRegExp( rule.pattern )
index = expression.indexIn( text )
while index >= 0:
length = expression.matchedLength()
self.setFormat( index, length, rule.format )
index = text.indexOf( expression, index + length )
self.setCurrentBlockState( 0 )
This process is repeated until the last occurrence of the pattern in the current text block is found. For rules that apply over multiple blocks or lines, further logic is needed. For an example, see the QSynatxHighlighter documentation. In order to apply the syntax highlighter to a QTextEdit, we simply create an instance of our QSyntaxHighlighter subclass, and pass it the QTextEdit or QTextDocument that we want the syntax highlighting to be applied to, as the following test application demonstrates:
class TestApp( QMainWindow ):
def __init__(self):
QMainWindow.__init__(self)
editor = QTextEdit()
highlighter = MyHighlighter( editor )
self.setCentralWidget( editor )
self.setWindowTitle( "Syntax Highlighter Example" )
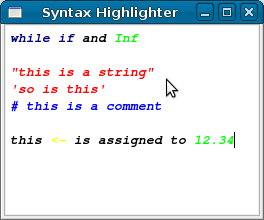
Once implemented, the above example produces output like this: